|
||||
|
|
звонок бесплатный
Наши сотрудники:
[email protected]
Екатерина - специалист по продаже а/м КАМАЗ
 [email protected]
[email protected]






Техника в наличии

Тягач КАМАЗ 44108-6030-24
2014г, 6х6, Евро3, дв.КАМАЗ 300 л.с., КПП ZF9, бак 210л+350л, МКБ,МОБ,рестайлинг.
цена 2 220 000 руб.,

КАМАЗ 4308-6063-28(R4)
4х2,дв. Cummins ISB6.7e4 245л.с. (Е-4),КПП ZF6S1000, V кузова=39,7куб.м., спальное место, бак 210л, шк-пет,МКБ, ТНВД BOSCH, система нейтрализ. ОГ(AdBlue), тент, каркас, рестайлинг, внутр. размеры платформы 6112х2470х730 мм
цена 1 950 000 руб.,

Самосвал КАМАЗ 6520-057
2014г, 6х4,Евро3, дв.КАМАЗ 320 л.с., КПП ZF16, ТНВД ЯЗДА, бак 350л, г/п 20 тонн, V кузова =20 куб.м.,МКБ,МОБ, со спальным местом.
цена 2 700 000 руб.,

Самосвал 6522-027
2014, 6х6, дв.КАМАЗ 740.51,320 л.с., КПП ZF16,бак 350л, г/п 19 тонн,V кузова 12куб.м.,МКБ,МОБ,задняя разгрузка,обогрев платформы.
цена 3 190 000 руб.,
СУПЕР ЦЕНА
на АВТОМОБИЛИ КАМАЗ
| 43118-010-10 (дв.740.30-260 л.с.) | 2 220 000 |
| 43118-6033-24 (дв.740.55-300 л.с.) | 2 300 000 |
| 65117-029 (дв.740.30-260 л.с.) | 2 200 000 |
| 65117-6010-62 (дв.740.62-280 л.с.) | 2 350 000 |
| 44108 (дв.740.30-260 л.с.) | 2 160 000 |
| 44108-6030-24 (дв.740.55,рест.) | 2 200 000 |
| 65116-010-62 (дв.740.62-280 л.с.) | 1 880 000 |
| 6460 (дв.740.50-360 л.с.) | 2 180 000 |
| 45143-011-15 (дв.740.13-260л.с) | 2 180 000 |
| 65115 (дв.740.62-280 л.с.,рест.) | 2 190 000 |
| 65115 (дв.740.62-280 л.с.,3-х стор) | 2 295 000 |
| 6520 (дв.740.51-320 л.с.) | 2 610 000 |
| 6520 (дв.740.51-320 л.с.,сп.место) | 2 700 000 |
| 6522-027 (дв.740.51-320 л.с.,6х6) | 3 190 000 |

подробнее про услугу перегона можно прочесть здесь.

|
Нужны самосвалы? Обратите внимание на Ford-65513-02. |
КАМАЗы в лизинг
ООО «Старт Импэкс» имеет возможность поставки грузовой автотехники КАМАЗ, а так же спецтехники на шасси КАМАЗ в лизинг. Продажа грузовой техники по лизинговым схемам имеет определенные выгоды для покупателя грузовика. Рассрочка платежа, а так же то обстоятельство, что грузовики до полной выплаты лизинговых платежей находятся на балансе лизингодателя, и соответственно покупатель автомобиля не платит налогов на имущество. Мы готовы предложить любые модели бортовых автомобилей, тягачей и самосвалов по самым выгодным лизинговым схемам.Контактная информация.
г. Набережные Челны, Промкомзона-2, Автодорога №3, база «Партнер плюс».
тел/факс (8552) 388373.
Схема проезда
Цепной траншейный экскаватор. Цепной траншейный экскаватор
Устройство и технические характеристики цепного траншейного экскаватора и дреноукладчика
Строительные машины и оборудование, справочник

Категория:
Эксплуатация экскаваторов
 Устройство и технические характеристики цепного траншейного экскаватора и дреноукладчика
Устройство и технические характеристики цепного траншейного экскаватора и дреноукладчикаЦепные траншейные экскаваторы предназначены для отрывки траншей в грунтах I—III категорий. Они отрывают траншеи с ровными стенками и дном, поэтому перед укладкой трубопроводов или кабелей не требуется дополнительных планировочных работ. Отвалы грунта располагаются в непосредственной близости от бровки траншеи, что удобно для последующей засыпки.
Промышленность выпускает цепные траншейные экскаваторы различные как по компоновке, так и по конструкции рабочего оборудования. Экскаваторы на пневмоколесном ходу выпускают на базе колесных тракторов, экскаваторы на гусеничном ходу — на базе гусеничных тракторов или собственных гусеничных шасси. Рабочее оборудование экскаваторов ЭТЦ-161, ЭТЦ-165, ЭТЦ-252 и ЭТУ-354А скребковое, а экскаватора ЭТУ-354 — ковшовое.
Рабочее оборудование экскаватора ЭТЦ-161 состоит из цепного рабочего органа скребкового типа и шнекового конвейера. Спереди на трактор устанавливают бульдозерный отвал. Привод рабочего оборудования предусмотрен от вала отбора мощности трактора через редуктор с муфтой предельного момента. Привод рабочего хода осуществляется гидростатической передачей, бесступенчатое регулирование рабочей скорости производится с помощью регулятора потока.
Экскаватор ЭТЦ-165 выполнен на базе универсального колесного трактора МТЗ-82. Два ведущих моста базового трактора обеспечивают высокие тягово-сцепные качества экскаватора. Автоблокировка дифференциала заднего моста снижает буксование и улучшает прямолинейность движения машины при работе экс-кавационным и бульдозерным оборудованием.
Возможность поворота бульдозерного отвала в плане и выдвижение его в сторону за колею трактора позволяют производить засыпку при движении параллельно траншее, что резко повышает производительность.
Экскаваторов ЭТУ-354, ЭТУ-354А и ЭТЦ-252 предназначены для отрывки траншей прямоугольного и трапецеидального сечения глубиной до 3,5 м, шириной по дну до 1,1 м и шириной по верху до 2,8 м в грунтах I—III категорий с каменистыми включениями размером до 200 мм. Цепные откосообразователи экскаватора ЭТУ-354А оснащены поперечными цепями, что обеспечивает более эффективное обрушение грунта.
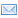
Рис. 1. Экскаватор ЭТЦ-161: 1 — зачистное устройство, 2 — рабочий орган, 3 — редуктор привода рабочего органа, 4 —турасный вал, 5 — гидромеханический ходоуменьшитель, 6 — трактор «Беларусь» МТЗ-50, 7 — гидроцилиндр подъема бульдозера, 8 —бульдозер, 9 — шиековый конвейер
На экскаваторах ЭТУ-354 и ЭТУ-354А применяют сменное оборудование, предназначенное для разработки мерзлых грунтов с глубиной промерзания до 1 м.
Экскаватор ЭТЦ-252, который заменяет экскаваторы ЭТУ-354 и ЭТУ-354А, имеет ряд преимуществ перед ними: более мощный двигатель, удобная кабина машиниста, бесступенчатое регулирование скоростей рабочего хода, рациональная навеска рабочего органа, гидропривод конвейера. Бее это позволяет улучшить условия труда машиниста, резко повысить производительность, улучшить приспособляемость экскаватора к грунтовым условиям.
Цепные траншейные экскаваторы обычного исполнения не могут разрабатывать прочные и мерзлые грунты, поэтому для выполнения этих работ создается специальный экскаватор ЭТЦ-208.
Рабочее оборудование этой машины представляет собой гусеничную цепь, оснащенную резцами и скалывающими клиньями. Рабочее оборудование и поперечный конвейер приводятся от вала отбора мощности трактора через специальный редуктор. Привод рабочего хода обеспечивается гидромеханическим ходо-уменьшителем.
Экскаватор-дреноукладчик представляет собой цепной траншейный экскаватор со специальным оборудованием и системами для строительства закрытого горизонтального дренажа (табл. 19). В зонах избыточного увлажнения используют экскаваторы-дреноукладчики ЭТЦ-202 и ЭТЦ-202А, которые отрывают траншею шириной 0,5 м в грунтах I—II категорий с наличием отдельных камней размером до 35 см.
Экскаваторы-дреноукладчики оснащены системами автоматического выдерживания заданного уклона дна траншеи, что позволяет укладывать дренаж как на ровной местности, так и на трассах с поперечным уклоном до 3, с продольным до 5° и при наличии местных неровностей до 15 см. Экскаваторы имеют ковшовое рабочее оборудование и ленточный отвальный конвейер.
Экскаватор-дреноукладчик ЭТЦ-202А (рис. 38) является модернизированной моделью экскаватора ЭТЦ-202, оборудован универсальным трубоукладчиком, который позволяет укладывать как керамические, так и пластмассовые дренажные трубы. Экскаватор имеет гидромеханическую трансмиссию рабочего передвижения, обеспечивает разгрузку грунта на любую сторону.
Для строительства дренажа в зонах искусственного орошения созданы экскаваторы-дреноукладчики с глубиной копания до 4 м. В настоящее время для укладки дренажа глубиной до 4 м применяют дреноукладчики типа ЭД-3,0; Д-658 и Д-659.
Экскаваторы-дреноукладчики типа Д-659, получившие наибольшее распространение, представляют собой цепной траншейный экскаватор на гусеничном ходу со специальным оборудованием, предназначенный для строительства горизонтального дренажа глубиной до 4 м из гончарных труб диаметром 100—200 мм с одновременной изоляцией их песчано-гравийным фильтром и последующей засыпкой траншей грунтом. Тягач экскаватора сконструирован на базе узлов трактора Т-100М и роторного траншейного экскаватора ЭР-7А. Рабочий орган дреноуклад-чика Д-659А(Б) цепной ковшовый. Ковшовая цепь, звездочки турасного вала и огибные ролики унифицированы с соответствующими деталями экскаватора
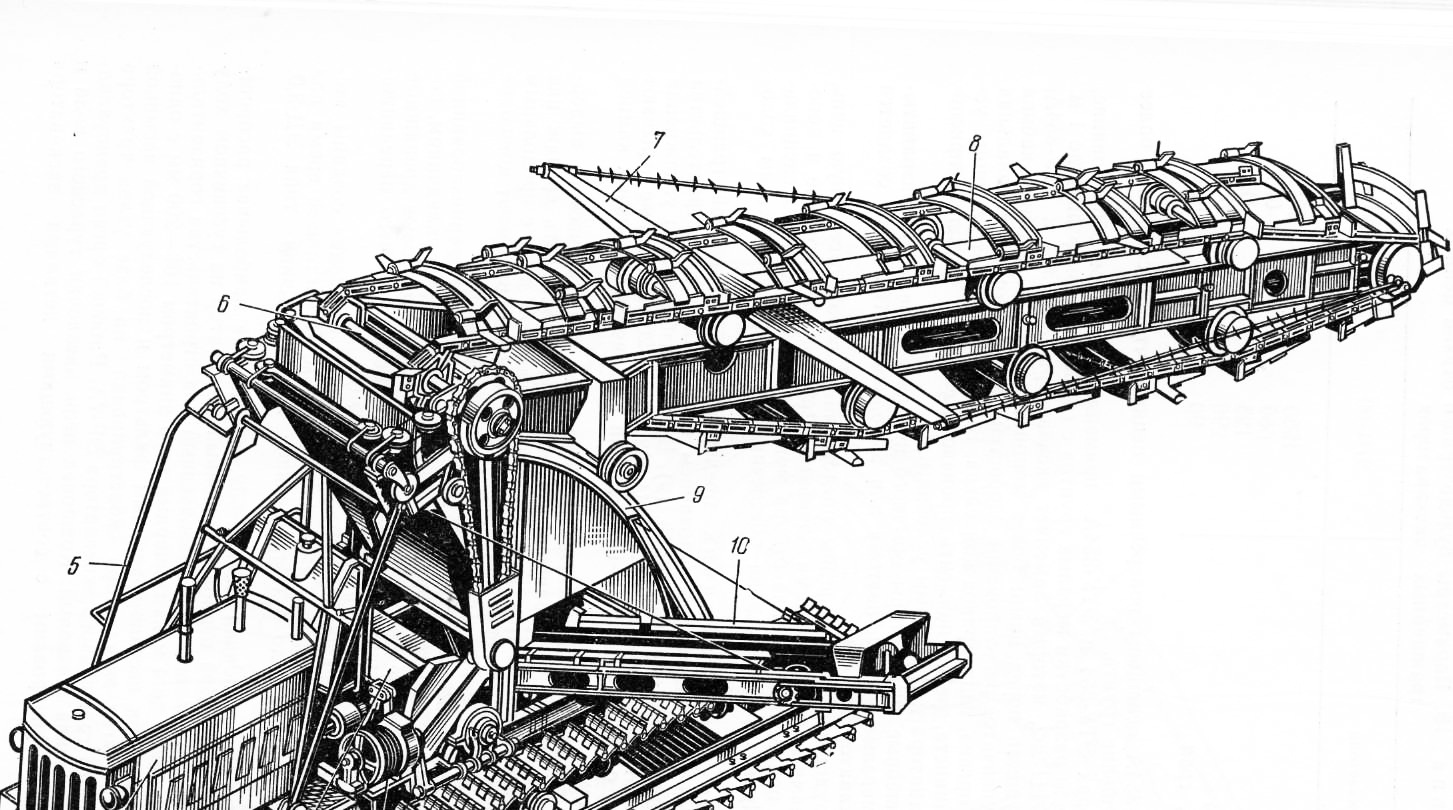
Рис. 2. Экскаватор ЭТУ-354А: 1 — гусеничный ход, 2 — лебедка, 3 -коробка передач, 4 — двигатель, 5— кабина, 6 — турасный вал, 7 — откосообразователи, 8 — рабочий орган, 9 — верхняя рама, 10 — конвейер
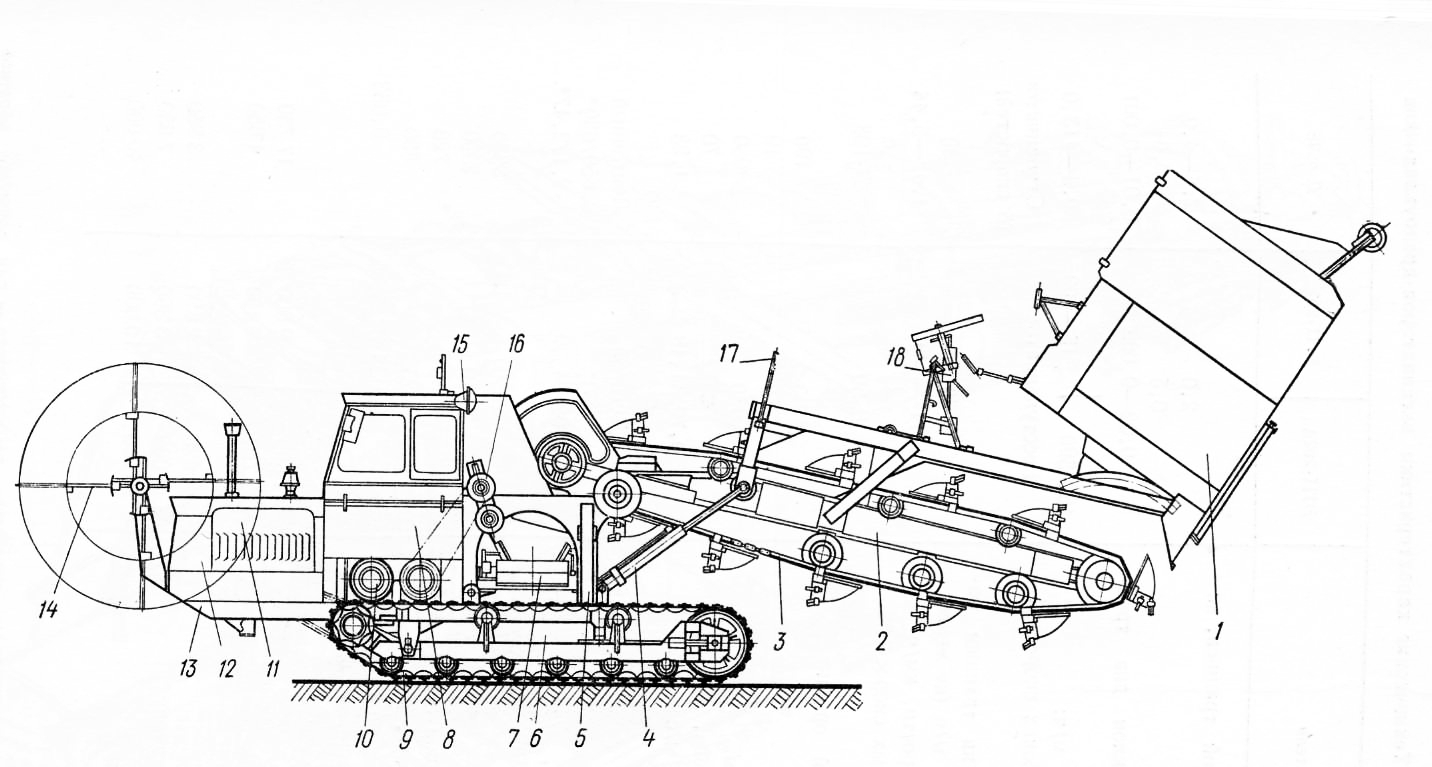
Рис. 3. Экскаватор-дреноукладчик ЭТЦ-202А: 1 — трубоукладчик, 2 — рама рабочего органа, 3 — ковшовая цепь, 4 — гидроцилиндр подъема рабочего органа, 5 — пилон, 6 — рама гусеничного хода, 7 — конвейер, 8 — кабина 9 — гусеничная цепь, 10 — бортовой фрикцион, 11 — капот, 12 – двигатель, 13 — рама экскаватора, И барабан для пластмассовых труб, 15 — фара, 16 — привод рабочего органа, 17 — направляющее кольцо для пластмассовых труб, 18 — датчик
Читать далее: Кинематические, гидравлические и электрические схемы цепного траншейного экскаватора и дреноукладчика
Категория: - Эксплуатация экскаваторов
Главная → Справочник → Статьи → Форум
stroy-technics.ru
роторные, цепные, гусеничные, малогабаритные и траншеекопатели мтз

Траншейный экскаватор – это землеройная спецмашина самоходного типа с непрерывным действием, имеющая в качестве рабочего органа многоковшовый или скребковый инструмент. В работе оставляет за собой выкопанную траншею конкретного профиля с одновременной транспортировкой из нее отработанного грунта. Траншейные экскаваторы стоят особняком среди рядов прочей спецтехники. Это происходит благодаря их специальному назначению и особенностям конструкции, позволяющим выполнять задачи, непосильные для других строительных и дорожно-строительных аппаратов.
Область применения траншейных экскаваторов
Назначение траншейных экскаваторов – подготовка ям, котлованов и траншей определенных размеров и формы для строительства различных объектов жилого, производственного либо дорожно-транспортного комплекса. Они используются на строительстве следующих объектов:
- Подземных коммуникаций различного назначения путем открытого рытья траншей:
- Трубопроводов для транспортировки воды, газа, нефти и т.п.,
- Централизованных систем отопления,
- Канализационных систем,
- Кабельных линий связи либо электроснабжения.
- Ленточных фундаментов большой протяженности для установки различных зданий и сооружений,
- Для создания ровных контуров будущих котлованов и других строительных выемок.
ИНТЕРЕСНО! Траншеекопатели, в отличие от одноковшовых экскаваторов, способны разрабатывать грунт абсолютно любого типа, даже мёрзлый и каменистый.
Особенности конструкции
Независимо от вида землеройного оборудования и особенностей самой машины, все траншейные экскаваторы сохраняют одинаковый набор основных частей:
- Базовый тягач пневмоколесного либо гусеничного типа, который обеспечивает равномерное поступательное передвижение всего агрегата,
- Рабочее оборудование роторного или цепного типа, закрепленное на машине навесным либо полуприцепным способом,
- Отвальное устройство, ссыпающее грунт в отвал либо транспортные средства для последующего вывоза,
- Дополнительное подъёмно-спусковое устройство для управления подъёмом и установкой в рабочее положение навесного оборудования.
Виды
Наиболее распространены классификации траншейных экскаваторов по виду самого тягача (колёсный или гусеничный) и по типу рабочего оборудования, где различают роторные и цепные машины.
Цепные
Цепные траншеекопатели (ЭТЦ) имеют рабочее оборудование в виде одно-либо двухрядной бесконечной (спаянной в кольцо) цепи. Она, огибая наклонную раму, несет на себе ряды ковшей или скребков определенной ширины.
Крепление цепи может быть:
- Свободное, с провисанием на поддерживающих и направляющих роликах,
- Жесткое на баровом рабочем органе машины.
При этом каждый из копающих ковшей оснащен режущим элементом и специальными откосообразователями, с помощью которых можно настраивать машину на рытье траншеи прямоугольного либо трапециевидного профиля.
Цепной траншейный экскаватор
В работе малогабаритного траншеекопателя цепи движутся поступательно сразу в двух направлениях: вокруг рамы или бара для отделения и транспортировки грунта, а также в сторону тягача для отрывания кусков грунта определенной глубины. С помощью цепного экскаватора можно получить глубину траншеи более 8-ми метров, а ширину – от 0,14 м и выше.
Роторные
Траншейные экскаваторы с рабочим органом роторного типа (ЭТР) разрабатывают грунт с помощью нескольких или одного жесткого колеса (ротора), на котором и размещены ковшовые резаки или зубья. Копка траншеи проходит при вращении этого колеса вокруг рамы на роликовых элементах с постепенным увеличением толщины снимаемой стружки от нуля до максимума.
ВАЖНО! Преимущество использования роторного траншеекопателя – возможность разработки пнистых грунтов благодаря превращению ротора в диско-фрезерный элемент при замене ковшей зубьями.
Роторная машина может прокапывать траншеи глубиной до 3-х и шириной от 0,8 до 2,5 метров. Она имеет более высокий КПД и большую производительность работы, чем цепная, но рытье более глубоких траншей для неё проблематично, т.к. влечет за собой сильное увеличение массы и габаритов навесного оборудования.
На фото роторный траншеекопатель
Гусеничные
Траншейные экскаваторы производятся на базе колёсных или гусеничных спецмашин. При этом тягачи на гусеничной основе дают такие преимущества, как:
- Большую проходимость и сцепление с грунтом.
- Более высокую мощность, при этом мощностные возможности рекордсменов достигают 1500 л.с.
- Возможность как наклонного, так и вертикального расположения рамы с режущими элементами.
Вертикально расположенная рама расширяет область применения экскаватора, позволяя копать траншеи на холмистой местности и склонах.
- Смещение рамы относительно тягача для копки траншеи вдоль дороги, по правую либо левую сторону от неё.

Производители
Изготовлением траншейных экскаваторов занимаются компании по производству спецтехники как отечественного, так и зарубежного происхождения, с представительствами в разных странах мира.
Caterpillar
Caterpillar (США) – мировой лидер в изготовлении всевозможной спецтехники разного класса тяжести. Его модельные линейки включают наземные и подземные аппараты, используемые в разработке полезных ископаемых, а также сельскохозяйственных, строительных, карьерных и других подобных работах. Траншеекопатели Caterpillar предназначены для работы в строительстве для жилищных, сельскохозяйственных либо коммерческих целей. Они отлично справляются с выемкой неглубоких траншей для прокладки трубопроводов и кабеля.
Vermeer Manufacturing Company

Vermeer Manufacturing Company (США) представляет несколько модельных линеек экскаваторов (это несколько десятков моделей), включающих модификации на колёсном и гусеничном ходу, с оборудованием как цепного, также и роторного типа. Техника этой фирмы оборудована электронным управлением посредством микропроцессорной системы, которая синхронизирует действия тягача и рабочих органов машины. Благодаря этому упростились управление и диагностика машины. Кроме этого, некоторые модели оснащены лазерными системами для контроля глубины траншеи.
Case Corporation
Модельные линейки Case Corporation (Франция) для траншейных экскаваторов значительно уже, чем у «Vermeer». Это колёсные машины с планетарными мостами весом от 327-и до 5761 кг, имеющие в качестве основного либо дополнительного оборудования копатели цепного и дискового типа, а также бурильную установку и др.
ООО «Радицкий машиностроительный завод»
Радицкий завод (Россия, Брянск) производит экскаваторы роторного типа на базе гусеничных тракторов Т-170. Это колоссальная техника весом до 32-х тонн, дающая особенно большую ширину траншей и имеющая габаритные конвейеры для эвакуации отвала грунта. Отлично приспособлены к работе со сложными породами, содержащими мелкоабразивные частицы. Широкое применение находят в газо-и нефтепроводных работах.
ДГУП «Дмитровский экскаваторный завод»
Дмитровский завод представляет цепную технику с несколькими видами цепей зимнего и летнего вариантов, отличающихся по длине, ширине и величине зубца. Основной базовый трактор здесь – МТЗ-82. Есть модели, дающие траншею шириной до 110-ти см и глубиной до 1,5 м.
Цепной траншейный экскаватор ЭЦУ-150 на базе трактора МТЗ-82
ОАО «Михневский ремонтно-механический завод»
Михневский завод предлагает потребителям цепные экскаваторы как с «летними», так и с «зимними» цепями. Они отличаются шириной: 140 мм для зимнего варианта и до 410-ти для летнего. Конструкторы завода постоянно усовершенствуют свою технику, добавляя новые элементы и возможности.
Последняя новинка «Михневцев» – двухбаровые траншеекопательные машины.
ОАО «Копейский машиностроительный завод»
Копейским заводом (Россия, Челябинск) выпускается горно-шахтное оборудование на цепной и баровой основе, приспособленное для работы с мёрзлыми грунтами. Модели имеют широкий диапазон веса и длины бара в стандартной поставке и широкий набор дополнительного навесного оборудования. Конструкция крепления навески очень проста и предполагает возможность замены её силами оператора.
magistraltrade.ru
Цепной траншейный экскаватор - WikiVisually
1. Ditch Witch – Ditch Witch, a trade name of Charles Machine Works, is an American brand of underground utility construction equipment, which has been in operation since 1949. The company is based in Perry, Oklahoma, innovation of Ditch Witch® machines started in the 1940s when a compact trenching machine was created to replace the pick and shovel for installation of underground residential utility services. The Ditch Witch® organization specializes in the design and manufacture of construction equipment. The company is a source for trenchers, vibratory plows, horizontal directional drilling systems, drill pipe, downhole tools, vacuum systems, fluid management systems. After Gus died in 1928, Charlie renamed the business Charlies Machine Shop, In 1944, Charlie persuaded his son, Edwin Ed, by then a mechanical engineer, Ed Malzahn learned from his elders the necessity of adapting a business to meet changing demands. In the late 1940s, he began to apply his engineering knowledge to inventing a device that he believed would be in great demand. At the time, the process of installing residential utility services—electric, gas and plumbing lines—involved slow, Malzahns idea was to create a compact trencher that would dramatically reduce the time and effort of this process. Working together, Ed and his father spent months in the machine shop creating the prototype of what would be known as the DWP. A 6-inch wide trench with a depth of 30 inches was the goal. The first production trencher rolled off the line in 1949. Called the endless conveyor ditch digging machine, It was the first mechanized and it was initially marketed for $750 per machine. Before the end of the 1950s, the company bought 160 acres of land west of Perry, in 1955, Ed Malzahns endless conveyor ditch digging machine received U. S. Alex Baker, a contractor from Long Island, New York. He used it to install sprinkler systems until he traded it in for a newer model in 1959. Ditch Witch company restored the older model to mint condition and put it on display in the Ditch Witch® museum in Perry, in 1958, Charles Machine Works incorporated with Charlie and Ed Malzahn having equal control. During the same year, the first Ditch Witch international office opened in Australia, by 1969, customers included utility, telephone, and cable television companies, government agencies, and general contractors. Ditch Witch® remains a leader in the industry it essentially created, Charles Machine Works’ campus outside of Perry contains a 30-acre manufacturing plant as well as training, testing, research, and product development facilities. It employs more than 1,300 people, making the company the largest employer in Perry, the Ditch Witch® compact trencher has twice been named one of the 100 best American-made products in the world by Fortune magazine
2. Трактор – A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery used in agriculture or construction. Most commonly, the term is used to describe a farm vehicle that provides the power and traction to mechanize agricultural tasks, especially tillage, but nowadays a great variety of tasks. Agricultural implements may be towed behind or mounted on the tractor, the word tractor was taken from Latin, being the agent noun of trahere to pull. The first recorded use of the meaning an engine or vehicle for pulling wagons or ploughs occurred in 1901. In Canada and the USA, the word may refer to the road tractor portion of a tractor trailer truck. The first powered farm implements in the early 19th century were portable engines – steam engines on wheels that could be used to drive farm machinery by way of a flexible belt. Richard Trevithick designed the first semi-portable stationary steam engine for use, known as a barn engine in 1812. The truly portable engine was invented in 1839 by William Tuxford of Boston, a large flywheel was mounted on the crankshaft, and a stout leather belt was used to transfer the drive to the equipment being driven. In the 1850s, John Fowler used a Clayton & Shuttleworth portable engine to drive apparatus in the first public demonstrations of the application of cable haulage to cultivation. In parallel with the portable engine development, many engineers attempted to make them self-propelled – the fore-runners of the traction engine. In most cases this was achieved by fitting a sprocket on the end of the crankshaft and these experiments met with mixed success. The alteration was made by fitting a long driving chain between the crankshaft and the rear axle. The first half of the 1860s was a period of great experimentation but by the end of the decade the standard form of the engine had evolved. It was widely adopted for agricultural use, the first tractors were steam-powered plowing engines. They were used in pairs, placed on side of a field to haul a plow back. In Britain Manns and Garrett developed steam tractors for direct ploughing, in the United States, where soil conditions permitted, steam tractors were used to direct-haul plows. Steam-powered agricultural engines remained in use well into the 20th century until reliable internal combustion engines had been developed, in 1892, John Froelich invented and built the first gasoline/petrol-powered tractor in Clayton County, Iowa, USA. A Van Duzen single-cylinder gasoline engine was mounted on a Robinson engine chassis, after receiving a patent, Froelich started up the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company and invested all of his assets
3. Ковш (рабочий орган) – A bucket is a specialized container attached to a machine, as compared to a bucket adapted for manual use by a human being. It is a material handling component. The bucket has a volume as compared to other types of machine attachments like blades or shovels. The name bucket may have been coined from buckets used in water wheels, buckets in mechanical engineering can have a distinct quality from the traditional bucket whose purpose is to contain things. Larger versions of type of bucket equip bucket trucks to contain human beings, buckets in water-hauling systems in mines or, for instance. Buckets exist in a variety of sizes or shapes and they can be quite large like those equipping Hulett cranes, used to discharge ore out of cargo ships in harbours or very small such as those used by deep-sea exploration vehicles. The shape of the bucket can vary from the conical shape of an actual bucket to more scoop-like or spoon-like shapes akin to water turbines. The cross section can be round or square and this is the same shape of a domestic form, the one-piece-standing single element, but often with an augmented size. In early developments of mining, a simple bucket allowed easy insertion of both miners and construction materials such as pit props, and later extraction of miners and ore. Common terms used in parts of the world include, Bowk, Kibble, Hoppit. Latterly they have been called sinking buckets, as they are now used when sinking new mine shafts before insertion of the cage. Concrete buckets help deliver concrete on a site of a building by the means of a tower crane. They have an opening to allow concrete to flow out of the bucket when in-place. They are placed at the end of an arm and have to be made from a material that provides isolation from electricity, like fiber glass. There may be a door on the side of the bucket, excavator buckets are made of solid steel and generally present teeth protruding from the cutting edge, to disrupt hard material and avoid wear-and-tear of the bucket. Subsets of the excavator bucket are, the bucket, trenching bucket, A ditching bucket is a wider bucket with no teeth, 5–6 feet used for excavating larger excavations. A trenching excavator bucket is normally 6 to 24 in wide, the design is used in bucket-wheel excavators. The buckets in the wheel have to be made of material to withstand the resistance of the material it cuts through
4. Скребок – In archaeology, scrapers are unifacial tools that were used either for hideworking or woodworking purposes. e. Scrapers are typically formed by chipping the end of a flake of stone in order to one sharp side. Most scrapers are either circle or blade-like in shape, the working edges of scrapers tend to be convex, and many have trimmed and dulled lateral edges to facilitate hafting. One important variety of scraper is the scraper, a scraper shaped much like its namesake. This scraper type is common at Paleo-Indian sites in North America, Scrapers are one of the most varied lithic tools found at archaeological sites. The edge of the scraper that is extremely angled is the working edge and this edge is often used to soften hides or cleaning the meat off of the hides, in addition to being used for wood work. As the term suggests, this tool was scraped at the hide or wood in order to reach the end goal. Scrapers tended to be enough to fit comfortably in the hand. However, it is likely that scrapers were mounted on short handles even though it is very rare to find mounted scrapers. As scrapers are used they have to be resharpened in order to stay effective and this causes them to get progressively smaller as they are used, resharpened, used, resharpend, and used again. Consequently, the majority of the scrapers that are found on sites are ones that have been resharpened and used to the point of being no longer functional, the two main classifications of scrapers are either end scrapers or side scrapers. End scrapers have working edges on one or both ends of a blade or flake, whereas side scrapers have an edge along one of the long sides. There are a couple of types of scrapers based on their use when it comes to wood and hide or based on the shape. The grattoir is a type of scraper made usually made of flint and its uses were to work wood. This type of scraper has its working edge along the axis of the blade. The nose scraper typically has a working edge either at both ends or just one end. This type of scraper is made from a blade and is used in more fine tuning work. The hollow scraper is a type of scraper that has a notch worked into the side or end of the scraper, tool size, This can be determined by either weight or dimensions and typically divided into either large or small scrapers
5. Канализация – Sewerage is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, Sewerage ends at the entry to a sewage treatment plant or at the point of discharge into the environment. It is the system of pipes, chambers, manholes, etc. that conveys the sewage or storm water, according to this definition, sewerage and sewage are two different terms. However, at least in American English colloquial usage, both terms are used interchangeably. The main part of a system is made up of large pipes that convey the sewage from the point of production to the point of treatment. In certain areas it has resulted in a significant lowering of the water table, in the example of Belgium, a lowering of the water table by 100 meters has been the result. The freshwater that is accumulated by the system is then piped to the sea. In areas where this is a concern, vacuum sewers may be used due to the shallow excavation that is possible for them. Severe constraints are applied to sewerage, which may result in premature deterioration and these include root intrusion, joint displacement, cracks and holes formation leading to a significant volume of leakage with an overall risk for the environment and public health. For example, it is estimated that 500 million m3 of contaminated water per year can leak into soil, the rehabilitation and replacement of damaged sewers is very costly. Annual rehabilitation costs for Los Angeles County are about €400 million, and in Germany, hydrogen sulfide is indirectly responsible for biogenic sulfide corrosion and consequently, sewerage need rehabilitation works. Various repairs options are available to Owners over a range of costs. Depending of the condition and contamination, the cleaning can range from simple high pressure jet water cleaning up to real hydro-demolition. One method to ensure sound concrete is exposed is to verify that the surface pH is superior to 10, as for any concrete repair, the state-of-the-art rules must be followed. It utilizes classical facade rotor pump, easily available in the market, the main drawback is the limited pumping distance that cannot exceed 75 meters. Spinning head wet spray, this method is similar to the first and this method is fast and especially suited for cylindrical chambers like manholes. When a structure is so severely corroded that man entry is a risk, high pressure dry spray, this method, also called “shotcrete” or “gunite” is allowing a faster rate of rehabilitation, and also to make a thicker application in a single pass. The main interest of dry shotcrete is the capacity to pump the mortar over a long distance, longest dry shotcrete distance the authors are aware is a job site in Australia in 2014 where 100% calcium aluminate mortar was air transported over 800 meters before being sprayed
6. Силовой кабель – A power cable is an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power, power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Flexible power cables are used for devices, mobile tools. The first power system developed by Thomas Edison in 1882 in New York City used copper rods, wrapped in jute. Although vulcanized rubber had been patented by Charles Goodyear in 1844, it was not applied to cable insulation until the 1880s, rubber-insulated cable was used for 11,000 volt circuits in 1897 installed for the Niagara Falls power project. Mass-impregnated paper-insulated medium voltage cables were commercially practical by 1895, during World War II several varieties of synthetic rubber and polyethylene insulation were applied to cables. Large single insulated conductors are sometimes called power cables in the industry. Cables consist of three components, conductors, insulation, protective jacket. The makeup of individual cables varies according to application, Cables for direct burial or for exposed installations may also include metal armor in the form of wires spiralled around the cable, or a corrugated tape wrapped around it. The armor may be made of steel or aluminum, and although connected to ground is not intended to carry current during normal operation. Power cables use stranded copper or aluminum conductors, although small power cables may use solid conductors, the cable may include uninsulated conductors used for the circuit neutral or for ground connection. The overall assembly may be round or flat, non-conducting filler strands may be added to the assembly to maintain its shape. Special purpose power cables for overhead or vertical use may have elements such as steel or Kevlar structural supports. Some power cables for outdoor overhead use may have no overall sheath, other cables may have a plastic or metal sheath enclosing all the conductors. The materials for the sheath will be selected for resistance to water, oil, sunlight, underground conditions, chemical vapors, impact, in nuclear industry applications the cable may have special requirements for ionizing radiation resistance. Cable materials may be specified not to large amounts of smoke if burned. Cables intended for use or direct burial in earth will have heavy plastic or metal, most often lead sheaths. When cables must run where exposed to damage, they may be protected with flexible steel tape or wire armor
7. Минский тракторный завод – Minsk Tractor Works may refer to two entities, a plant in Minsk, Belarus and a plant association in Belarus. Minsk Tractor Works is an industrial enterprise in Minsk, Belarus. It is a part of the association Производственное объединение Минский тракторный завод, or Proizvodotvennoe Obiedinenie Minskiy Traktorniy Zavod, in addition to the main plant in Minsk, the association includes a number of plants that produce parts and attachable tools for tractors and other vehicles produced by MTZ. The plant was established on May 29,1946, the first tractor, the MTZ-2 model, was manufactured on October 14,1953. As of 2005 it had nearly 20,000 workers, the plant produces over 62 models of vehicles. Its main civil production has been four-wheeled tractors of model MTZ, by 1995 the plant manufactured 3,000,000 tractors. In 1999 it produced 58% of all manufactured in CIS. For several years the plant has been holding 8-10% share of the market of wheeled tractors. Mtz tractors were exported to western Europe. The most popular exported model was Mtz-50, there were no major differences between the exported ones and not exported ones, but one major difference was that the exported tractors were painted red. Since 2000 the tractors of the plant manufactured for export have been certified for the European Union, during their operation in the era of the Soviet Union, they have been awarded the collective titles of the Order of Lenin and the Order of the October Revolution. Since 2010, distribution of Belarus tractors in USA and Canada is carried on through a local distributor MTZ Equipment Ltd. Belarus-80.1, Belarus-82.3, Belarus-923.3, Belarus-1021, Belarus-Belarus-1025.21220.3, Belarus-1221.2, Belarus-1523, Belarus-2022.3, Belarus-3022DTS.1, belarus-80X, Belarus-100X, Belarus-920R, Belarus-921.3, BELARUS-921. 4-10 /91. Tractors would be exported to all ASEAN countries, until 2010 Minsk Tractor Works was a sponsor of a Belarusian Premier League football team MTZ-RIPO Minsk. Games were played at Traktor stadium, which is located near the plant, the Palace of Culture of the plant hosts the ballroom Dance Club Mara. MTZ official website Belarusian Machine Building, Once a Nations Pride, Now a Burden
8. Многоковшовый экскаватор – Bucket chain excavators are heavy equipment used in surface mining and dredging. It uses buckets on a chain to remove large quantities of material. It has similar characteristics to bucket-wheel excavators and trenchers and they remove material from below their plane of movement, which is useful if the pit floor is unstable or underwater. The first documented use of a bucket chain excavator was in 1859 and it was developed by Alphonse Couvreux, a French entrepreneur. The excavators from Couvreux were used in the construction of the Suez Canal
9. Траншея – A trench is a type of excavation or depression in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide, and narrow compared with its length. In geology, trenches are created as a result of erosion by rivers or by geological movement of tectonic plates, in the civil engineering field, trenches are often created to install underground infrastructure or utilities, or later to access these installations. Trenches have also often been dug for defensive purposes. In archaeology, the method is used for searching and excavating ancient ruins or to dig into strata of sedimented material. Some trenches are created as a result of erosion by running water or by glaciers, others, such as rift valleys or more commonly oceanic trenches, are created by geological movement of tectonic plates. Some oceanic trenches include the Mariana Trench and the Aleutian Trench, the former geoform is relatively deep, linear and narrow, and is formed by plate subduction when plates converge. In the civil engineering field of construction or maintenance of infrastructure and they are used to place underground easily damaged and obstructive infrastructure or utilities. A similar use for higher bulk would be in pipeline transport and they may also be created later to search for pipes and other infrastructure that is known to be underground in the general area, but whose exact location has been lost. Finally, trenches may be created as the first step of creating a foundation wall, Trench shoring is often used in trenchworks to protect workers and stabilise embankments. An alternative to digging trenches is to create a utility tunnel, the advantages of utility tunnels are the reduction of maintenance manholes, one-time relocation, and less excavation and repair, compared with separate cable ducts for each service. When they are well mapped, they also allow access to all utilities without having to dig access trenches or resort to confused. One of the greatest advantages is public safety, for a comparison of utility tunnels vs. direct burial, see the article referred to above. In some cases, a trench is dug and deliberately preserved. This is typically done to install depressed motorways, open railway cuttings, trenches have often been dug for defensive purposes. In the pre-firearm eras, they were mainly a type of hindrance to an attacker of a fortified location, an early example of this can be seen in the Battle of the Trench, one of the early Battles of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad. With the advent of firearms, trenches were used to shelter troops. The advantage of this method is that it only a small part of the site. However, this also has the disadvantage of only revealing small slices of the whole volume
10. Дренаж – Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of surface and sub-surface water from an area. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging, all houses in the major cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro had access to water and drainage facilities. Waste water was directed to covered drains, which lined the major streets, the invention of hollow-pipe drainage is credited to Sir Hugh Dalrymple, who died in 1753. New drainage systems incorporate geotextile filters that retain and prevent fine grains of soil from passing into, geotextiles are synthetic textile fabrics specially manufactured for civil and environmental engineering applications. Geotextiles are designed to retain fine soil particles while allowing water to pass through, in a typical drainage system they would be laid along a trench which would then be filled with coarse granular material, gravel, sea shells, stone or rock. The geotextile is then folded over the top of the stone, groundwater seeps through the geotextile and flow within the stone to an outfell. In high groundwater conditions a perforated pipe is laid along the base of the drain to increases the volume of water transported in the drain. Alternatively, the prefabricated plastic drainage system made of HDPE called SmartDitch, often incorporating geotextile, over the past 30 years geotextile and PVC filters have become the most commonly used soil filter media. They are cheap to produce and easy to lay, with factory controlled properties that ensure long term filtration performance even in fine silty soil conditions, seattles Public Utilities created a pilot program called Street Edge Alternatives Project. The project focuses on designing a system to provide drainage that more closely mimics the natural landscape prior to development than traditional piped systems, the streets are characterized by ditches along the side of the roadway, with plantings designed throughout the area. An emphasis on non curbed sidewalks allows water to more freely into the areas of permeable surface on the side of the streets. Because of the plantings the run off water from the area does not all directly go into the ground. Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems are designed to encourage contractors to install drainage system that closely mimic the natural flow of water in nature. Since 2010 local and neighbourhood planning in the UK is required by law to factor SUDS into any development projects that they are responsible for, slot drainage has proved the most breakthrough product of the last twenty years as a drainage option. Both stainless steel and concrete channel slot drainage have become industry standards on construction projects, the civil engineer is responsible for drainage in construction projects. They set out from the all the roads, street gutters, drainage, culverts. During the construction process he/she will set out all the levels for each of the previously mentioned factors. Civil engineers and construction managers work alongside architects and supervisors, planners, quantity surveyors, typically, most jurisdictions have some body of drainage law to govern to what degree a landowner can alter the drainage from his parcel
wikivisually.com
423800, Набережные Челны , база Партнер Плюс, тел. 8 800 100-58-94 (звонок бесплатный)